Understanding the Interest Rate Cycle: How It Impacts Borrowing and Investing
Understanding the Interest Rate Cycle: How It Impacts Borrowing and Investing
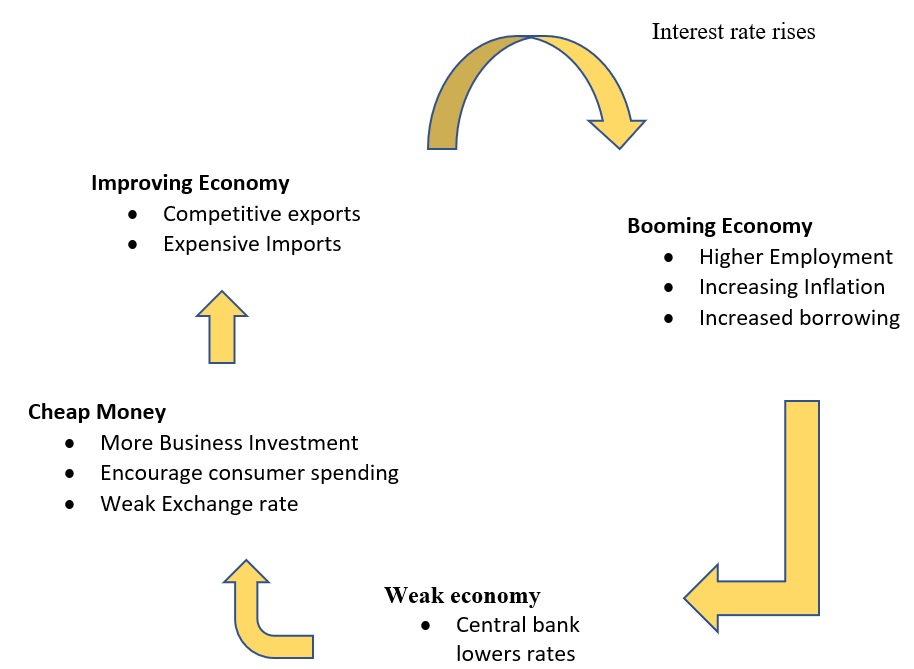
The interest rate cycle refers to the fluctuations in interest rates set by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States. These rate adjustments impact various economic variables, from borrowing costs to investment decisions. Whether you're a business owner, investor, or consumer, understanding the interest rate cycle can help you make smarter financial decisions.
How the Interest Rate Cycle Works
The interest rate cycle typically follows a pattern of expansion and contraction:
- During expansion, the economy grows, and the central bank may raise interest rates to control inflation.
- During contraction, the economy slows, and the central bank often lowers rates to stimulate growth.
One classic example is the Federal Reserve's response to the 2008 financial crisis. To boost the economy, the Fed lowered the federal funds rate—the interest rate at which banks lend to each other overnight—down to near zero. This move made borrowing more affordable, which encouraged businesses and consumers to take loans, ultimately boosting spending and investments.
How Interest Rate Changes Affect Borrowing
Let's break this down with a simple example:
- If the central bank sets the interest rate at 2% per year, a borrower who takes out a $100 loan would have to repay $102 after one year.
- If the central bank lowers the rate to 1% per year, the borrower only needs to repay $101, making borrowing more attractive and possibly encouraging larger loans.
- Conversely, if the central bank raises the rate to 3%, the borrower would need to repay $103, which might discourage borrowing.
The Broader Economic Impact
Changes in interest rates affect more than just borrowers. Lower interest rates can lead to:
- Increased borrowing and spending, which stimulates economic growth.
- However, low rates can also fuel asset bubbles and inflation if not carefully managed.
On the flip side, higher interest rates can:
- Help control inflation by slowing down spending.
- But they can also dampen economic growth, potentially leading to higher unemployment rates.
As former Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke noted, "The Federal Reserve's monetary policy tools can help promote employment and economic growth, but they also carry risks to the economy and financial system."
Conclusion: Making Informed Financial Decisions
Understanding the interest rate cycle is crucial for making informed financial decisions, whether you're borrowing, investing, or managing a business. By knowing how interest rates influence the economy, you can better anticipate changes and align your financial strategy with the broader economic environment.