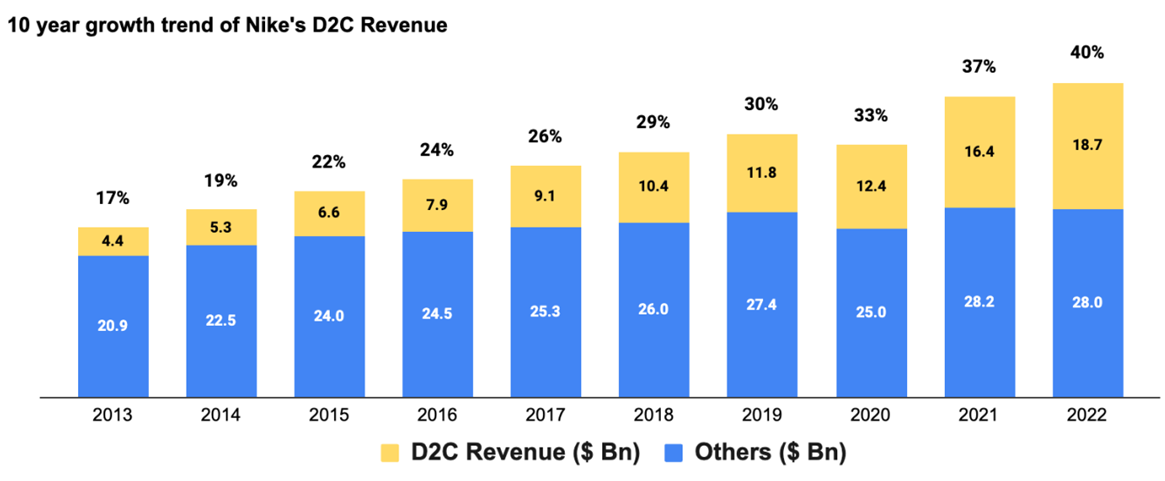
The Rise and Fall of Nike's D2C Strategy
Nike's Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) strategy represents a bold effort to forge a direct link with customers through owned retail and e-commerce channels. While the D2C model provides enhanced control over branding and pricing, it also necessitates substantial investments in infrastructure and marketing. Below are the key aspects of Nike's D2C journey, highlighting its successes, challenges, and the lessons learned.
Effective Distribution Channels
- Direct Engagement: Nike's D2C strategy primarily focused on engaging customers directly, bypassing traditional retail channels.
- Control Over Branding: By managing its own distribution, Nike could maintain brand integrity and set pricing without third-party influence.
Product Development for Success
- Digital Transformation: Nike's evolution included an emphasis on digital product development tailored for e-commerce, exemplified by the launch of innovative products like the Nike Adapt BB shoes, which feature automated lacing technology.
- Personalization: This focus on personalization helped Nike meet the growing demand for customized shopping experiences.
Impact of Recession on D2C Sales
- Pandemic Surge: The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed a significant increase in e-commerce sales, with Nike's D2C revenue soaring by 82% in Q2 2020.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Despite this growth, the accompanying recession triggered supply chain disruptions, resulting in inventory challenges that hampered sales potential.
Limitations of Direct-to-Consumer Approach
- Scalability Issues: While the D2C model offers advantages, it presents challenges in scalability and sustainability.
- High Operational Costs: The expenses linked to maintaining physical stores and robust e-commerce platforms posed significant challenges for profitability.
Inventory and Supply Chain Shocks in D2C
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The pandemic caused substantial inventory issues for Nike, affecting its ability to meet demand for popular products.
- Missed Opportunities: These supply chain problems led to missed sales opportunities, highlighting vulnerabilities in the D2C approach.
Direct-to-Consumer Business Strategies
- Customer Engagement: Nike's D2C strategy emphasized customer engagement through mobile apps, loyalty programs, and social media platforms.
- Data Analytics: By leveraging data analytics, Nike aimed to better understand customer preferences and enhance personalized marketing efforts.
Building a Thousand CR Company
- Long-Term Relationships: Nike's vision for its D2C strategy included creating lasting relationships with customers through tailored experiences and targeted marketing.
- Customer Relationship Focus: This "thousand-customer relationship" (CR) model underscores the importance of understanding customer needs.
Key Takeaways for D2C Founders
- Control and Investment: While the D2C model allows for more control over branding and pricing, it demands significant infrastructure and marketing investments.
- E-commerce Focus: Product development should prioritize e-commerce and personalization to align with modern consumer behavior.
- Inventory and Supply Chain Management: Effective inventory management and supply chain optimization are vital for sustaining a successful D2C strategy.
- Data-Driven Engagement: Prioritizing customer engagement and leveraging data analytics is crucial for cultivating long-term relationships.
Conclusion
Nike's D2C strategy illustrates both the potential rewards and inherent challenges of a direct consumer approach. Despite facing obstacles such as inventory management issues and high operational costs, Nike successfully established a direct connection with its customers, fostering personalized experiences through data-driven insights. The lessons learned from Nike’s journey can serve as a valuable guide for other companies venturing into the D2C landscape, emphasizing the need for a balanced approach to investment in infrastructure, product development, and inventory management.